The administration of 1C:Enterprise servers utility for Windows is intended for performing the following tasks:
- Creating, modifying, and deleting server clusters
- Modifying clusters: creating and deleting working servers, modifying their parameters, and specifying their requirements of functionality purpose
- Specifying cluster fault tolerance level
- Manual load balancing between working servers
- Managing the list of central server administrators in a cluster and the list of cluster administrators
- Monitoring user connections to Infobases and service connections
- Disconnecting users from Infobases
- Monitoring 1C:Enterprise object locks and client connection locks
- Real-time analysis of DBMS transaction locks
- Managing user-to-Infobase connection lockouts
- Managing scheduled job execution lockouts
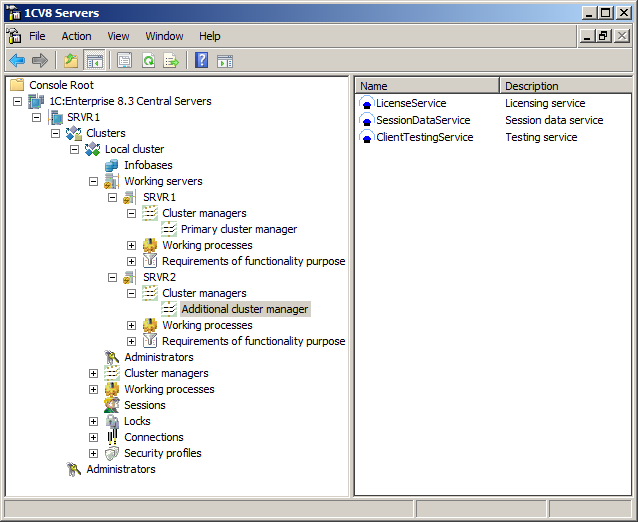
The utility is implemented as an MMC (Microsoft Management Console) snap-in, you can run it on any computer that has this software installed.
All 1C:Enterprise server administration features are also available in 1C:Enterprise script.
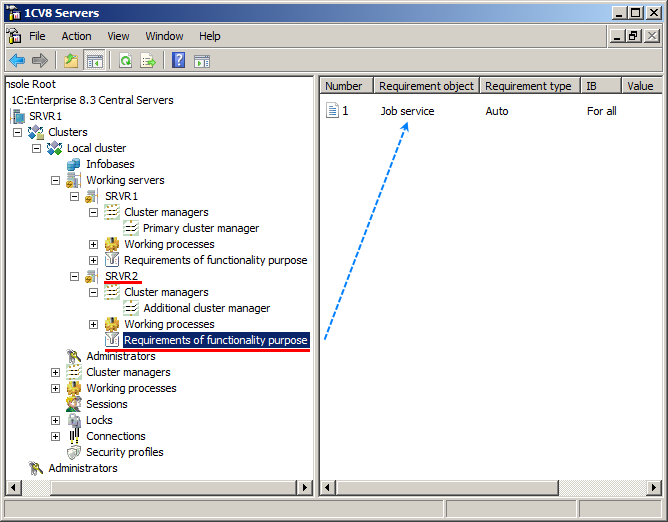
Requirements of functionality purpose
The administrator manages the cluster by specifying the list of computers (working servers) that form the cluster. They can also specify the requirements to the servers, if necessary: which services and Infobase connections are available on each working server. Cluster managers and working processes are started automatically based on the specified requirements. One can specify the requirements to working servers interactively using the cluster administration console, or using 1C:Enterprise script.
Fault tolerance level
One can specify the cluster fault tolerance level as a number of working server failures that do not interrupt the user's work. Backup services required to provide the desired fault tolerance are started automatically, and replication of each active service to backup ones is performed in real-time.
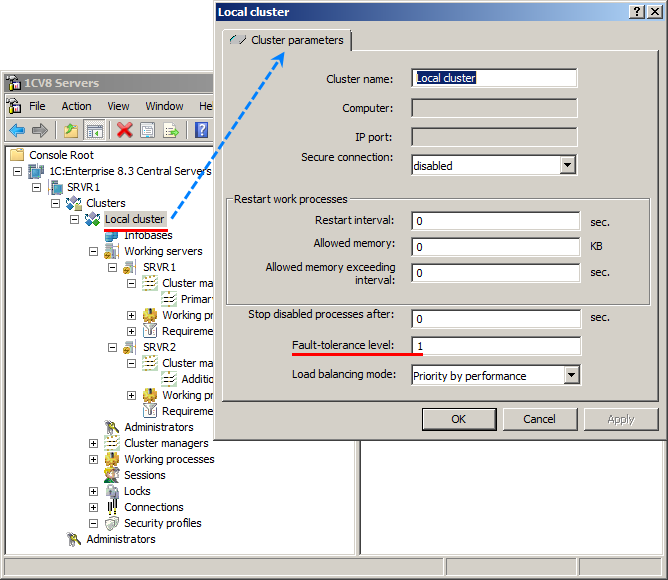
Manual load balancing
The load balancing between the working servers is based on real-time analysis of their performance capabilities. Manual load balancing is also available, this includes limiting the number of Infobases and connections processed by a single working process on a specific server.
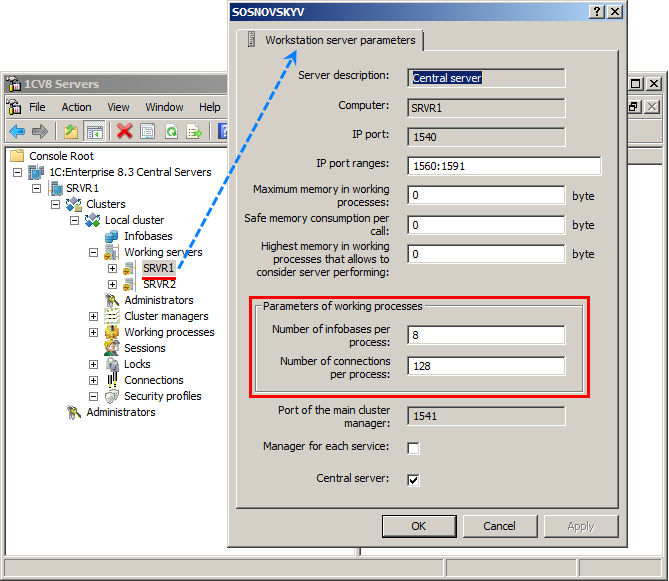
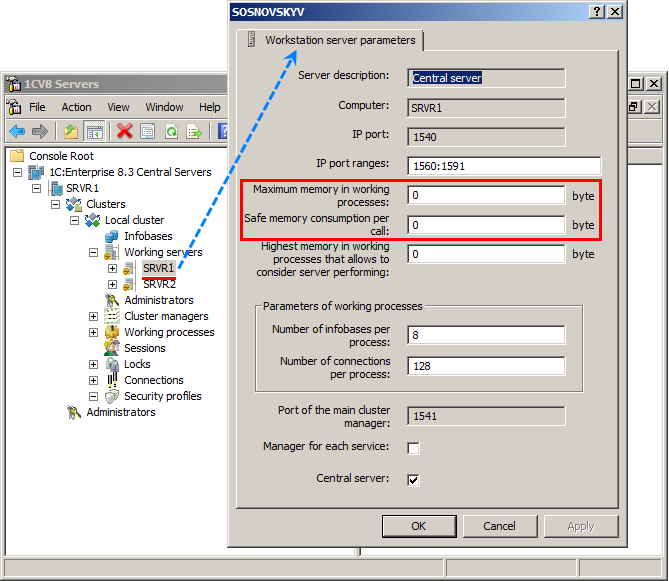
Limiting the amount of memory allocated for working processes
Limiting the amount of memory allocated for working processes is available. This includes limiting the total amount of memory for all working processes, as well as limiting the amount of memory for a single working process call. This increases the cluster fault tolerance against human-initiated malfunctions.
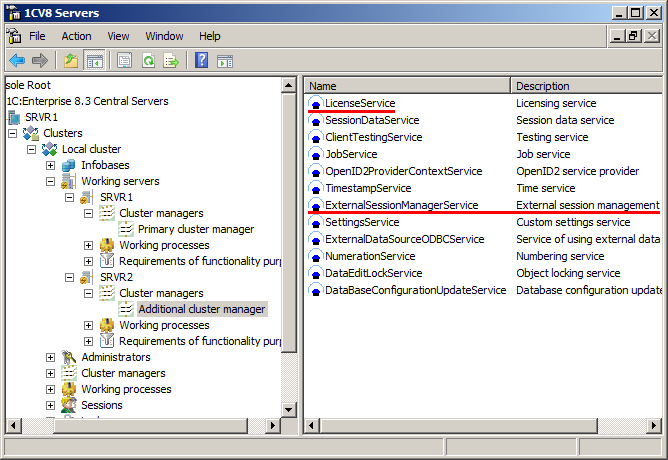
Licensing service and external session management service
The licensing service dispatches software licenses required to start client applications and 1C:Enterprise servers, so that administrators can freely configure any of the cluster working servers or deploy clusters on virtual servers whose parameters are subject to dynamic changes.
The external session management service limits the number of users connected to each Infobase. It notifies external systems when users connect to Infobases or disconnect from them, and receives responses that allow or deny connections. The interaction with external systems is performed using a web service that provides a certain set of methods.
Security profiles
Security profiles prevent applied solutions from performing potentially insecure operations that might impact the server cluster functioning.
A cluster administrator can assign any of the security profiles available in the cluster to an Infobase. This limits the set of potentially insecure operations to those allowed by the security profile.
A newly created profile with default settings prohibits all potentially unsafe operations:
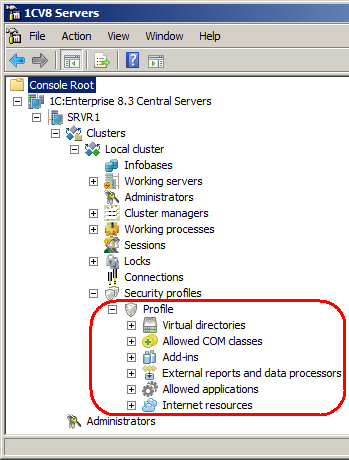
This includes:
- Accessing the server file system
- Running COM objects
- Using 1C:Enterprise add-ins
- Running external reports and data processors
- Running applications installed on the server
- Accessing Internet resources
So, when you run an applied solution that you do not yet know well, you can avoid all risks simply by creating an empty security profile and assigning it to the Infobase. Then you can fine-tune the security profile if necessary by adding allowed operations.
Next page: Configuration update
See also: