Support of Automation Server and Automation Client is one of the tools for integration with other software systems.
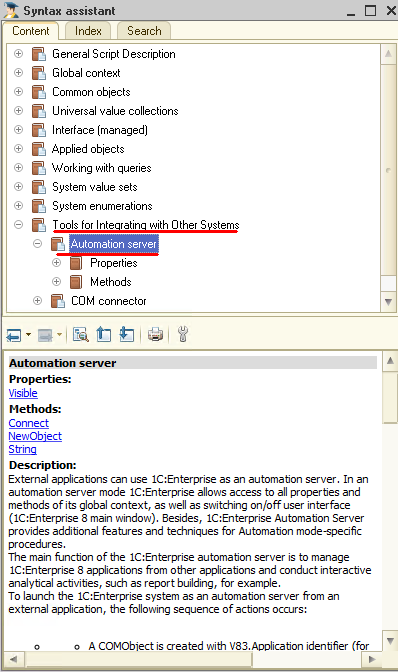
Automation Server
The key purpose of 1C:Enterprise's Automation Server is managing 1C:Enterprise's application from other applications and performing actions analogical to interactive actions.
1C:Enterprise's Automation Server grants access to all properties and methods of its global context, has additional properties and methods for performing actions specific to the Automation mode.
The developer has to do the following to launch 1C:Enterprise as the Automation Server from a third-party application:
-
create a COM object with ID V83.Application
-
initialize 1C:Enterprise with Connect ()
After that, the user can fetch 1C:Enterprise properties and methods as Automation Servers.
Example
' In this example the 1C:Enterprise configuration is launched and initialised
' in the c:\InfoBases\Trade directory
' Then we create an object of type "Catalog.Goods" in the 1C:Enterprise.
' Then we create new folder of items called "***** Export from Excel ******"
' Data from the MS Excel table is writen to the newly created catalog folder.
' The example uses MS Visual Basic.
Sub Excel_to_trade()
Dim trade As Object
Dim Goods As Object
Dim Group As Object
Dim Item As Object
Set trade = CreateObject("V83.Application")
trade.Connect("File=""c:\InfoBases\Trade"";Usr=""Director"";")
Set Goods= trade.Catalogs.Goods
Set Group = Goods.CreateFolder()
Group.Description = "***** Export from Excel ******"
Group.Write()
N = 100 'Count lines in the document
For Count = 1 To N
Set Item = Goods.CreateItem()
Item.Name = Application.Cells(Count, 2).Value
Item.Ret_Price = Application.Cells(Count, 3).Value
Item.Small_Wholesale_Price = Application.Cells(Count, 4).Value
Item.Wholesale_Price = Application.Cells(Count, 5).Value
Item.Parent = Group.Ref
Item.Write()
Next Count
End Sub
Execution Context
1C:Enterprise as an Automation Server may have the following properties:
-
system constants
-
values of objects set in the configurator accessed through managers (e.g. constants, enumerations, directories, documents, document journals, reports, processings, charts of characteristic types, charts of accounts, charts of calculation types, and registers)
-
variables defined in the application module
1C:Enterprise as an Automation Server may have the following methods:
-
system procedures and functions
-
procedures and functions of the application module and general modules, defined with the code word Export
-
two additional methods — Connect () and NewObject ()
Automation Client
As most advanced software solutions, 1C:Enterprise can act as an Automation Client. This said, 1C:Enterprise can refer to another 1C:Enterprise version (e.g. another configuration) to exchange data.
Here's an example: a query to 1C:Enterprise infobase from another 1C:Enterprise infobase. In this example, 1C:Enterprise with the database in c:\InfoBases\Trade is launched and initialized. Then, in this infobase, in Goods catalog, a new group is created — titled *** Export from another 1C:Enterprise infobase*** — and written.
Procedure Create()
// Create Automation Server
AutomationServer = New COMObject("V83.Application");
// Connect to InfoBase
AutomationServer.Connect("File=""c:\InfoBases\Trade"";Usr=""Director"";");
// Create a new group in catalog Goods and write it
CatalogProducts = AutomationServer.Catalogs.Goods;
NewGroup = CatalogProducts.CreateFolder();
NewGroup.Description = "***** Export from another 1C:Enterprise 8 infobase ******";
NewGroup.Write();
EndProcedure
Next page: HTML documents